University of Durham
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
-
The data consists of a spreadsheet containing rheology data for 39 samples of syrup, containing air bubbles and/or spherical glass particles. These data were used by Truby et al. (2014) to support a model for the rheology of a three-phase suspension. Each sample was placed in the rheometer (concentric cylinder geometry), and the stress was stepped up and then down, taking a measurement of strain rate at each step. Further details of the experiments may be found in Truby et al. (2014). NERC grant is NE/K500999/1. Co-author working with a NERC grant, NE/G014426/1.
-

Data relates to the NERC Urgency Grant NE/R00210X/1 which focusses on Sediment signatures of the 25 December 2016 Chile earthquake to constrain detection limits of tidal marsh records. The documentation provides an overview of findings from two field seasons to the southern coast of Isla de Chiloé, Chile, including field observations, sediment samples and surface vegetation surveys. The research locations for diatom analyses are Ayentema, Asasao, Inio and Quilanlar, southern Chiloé, Chile. Field season 1 (excluding travel dates): 2-9 August 2017 Field season 2 (excluding travel dates): 6-16 October 2017 Diatom data collection: through to 30 June 2018
-
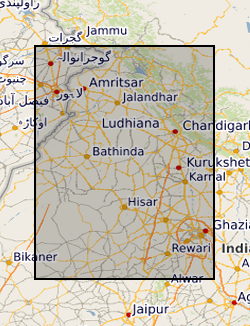
Groundwater level measurements collected by the state groundwater boards of Punjab and Haryana states, India, and by the Central Groundwater Board. The data consist of well locations and measurements of groundwater levels, in metres below the top of the well casing. Data were collected in both the pre-monsoon (May-June) and post-monsoon (October-November) periods. Data availability is irregular across the entire suite of wells.
-
Neodymium (Nd) concentrations, Nd radiogenic isotopes (143Nd/144Nd) and Nd stable isotopes (d146/144Nd) for chondritic meteorites, terrestrial basalts and mantle rocks, and rock reference materials.
-
This project is aimed at understanding what kind of conditions the Earth's core formed under and how this affected the amount of oxygen present in the rocky interior of the Earth. It uses experiments which simulate the very high pressures and temperatures that would have been present in the Earth's interior when the core formed, combined with very precise chemical analyses of these experiments. From these results I will learn how certain chemical elements distributed themselves between the metal core and the rocky outer part of the Earth, and whether this distribution behaviour changes with different conditions and with the amount of oxygen present. By comparing the results I get from the experiments with the chemical compositions of rocks from the Earth and very primitive meteorites we will be able to understand better how the Earth's core formed, and how this may have affected the chemistry of our planet and the development of its atmosphere and oceans. Four papers are linked to this grant: Stable chromium isotopic composition of meteorites and metal-silicate experiments: Implications for fractionation during core formation Unlocking the zinc isotope systematics of iron meteorites Iron isotope tracing of mantle heterogeneity within the source regions of oceanic basalts Isotopic evidence for internal oxidation of the Earth's mantle during accretion
-
Data generated using freely-available satellite remote sensing observations from the USGS Earth Resources Observation Science Centre, together with a freely-available ice margin chronology from Dyke et al. (2003) Geological Survey of Canada Open File Report No. 1574. The map is published in the Journal of Maps: http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/17445647.2014.912036 Published article in 'Nature' Volume 530 Feb 2016 with associated source data. https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature16947 Published paper in the Taylor Francis Online Journal with associated data. https://dx.doi.org/10.1080/17445647.2014.912036
-
Due to differential loading of ice on Britain and Ireland the glacial isostatic adjustment (GIA) response and therefore sea-level record will vary with distance from the centre of the British Irish Ice Sheet. GIA models are tested against geological observations, however there is a paucity of observations below -10m depth and the lateglacial period when the BIIS retreated leading to a rapid response of both sea-level and GIA. The aim of the project was to use geophysical data, ground truthed by core material, to find evidence of lateglacial sea-level minima in the Irish and Celtic Sea to refine these GIA models. Cruise log and digital copies of the core information (location, water depth, core length) taken onboard the research cruise CE12008 on the RV Celtic Explorer. A GeoReseource 6m vibrocorer was used to collect sediment samples. Cores where taken at multiple sites and from southern and eastern Ireland: Bantry Bay, Dunmanus Bay, Waterford,Offshore County Louth and Dundalk Bay, offshore Isle of Man; offshore Wales: Cardingan Bay; and offshore Northern Ireland: Kilkeel and Dundrum Bay, Belfast Lough.
-
This dataset contains major element, trace element and isotopic analyses for samples collected during the NERC project "Orogenic Plateau Magmatism" (NE/H021620/1) (2011-2014). Samples are late Cenozoic volcanic rocks erupted across centres of the Iranian or Armenian sectors of the Turkish-Iranian Plateau, during the ongoing Arabia-Eurasia continental collision. Results have been published in the following papers: Allen, M.B., Kheirkhah, M., Neill, I., Emami, M.H. & McLeod, C.L. (2013) Generation of arc and within-plate chemical signatures in collision zone magmatism: Quaternary lavas from Kurdistan Province, Iran. Journal of Petrology, 54,887-911. Kheirkhah, K., Neill, I., Allen, M.B. & Ajdari, K. (2013) Small-volume melts of lithospheric mantle during continental collision: late Cenozoic lavas of Mahabad, NW Iran. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 74, 37-49. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.06.002. Kheirkhah, K., Neill, I. & Allen, M.B. (2015) Petrogenesis of OIB-like basaltic volcanic rocks in a continental collision zone: Late Cenozoic magmatism of Eastern Iran. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 106, 19-33. Neill, I., Meliksetian, K., Allen, M.B., Navasardyan, G. & Kuiper, K. (2015) Petrogenesis of mafic collision zone magmatism: The Armenian sector of the Turkish-Iranian Plateau. Chemical Geology, 403, 24-41. Neill, I., Meliksetian, K., Allen, M.B., Navarsardyan, G. & Karapetyan, S. (2013) Pliocene-Quaternary volcanic rocks of NW Armenia: magmatism and lithospheric dynamics within an active orogenic plateau. Lithos, 180-181, 200-215.
-
Tables of characteristic parameters for each model used in paper Agrusta et al. 2014, The effect of metastable pyroxene on the slab dynamics, DOI: 10.1002/2014GL062159 Tables of characteristic parameters for each model used in paper Agrusta et al 2017, Subducting-slab transition-zone interaction: Stagnation, penetration and mode switches, DOI: 10.1016/j.epsl.2017.02.005
-
Apatite as a quantitative tool for tephrochronology and magmatic evolution (NERC grant NE/K003852/1)
Documentation of experiments run to investigate partitioning of H-C-F-Cl (Hydrogen, Carbon, fluorine, Chlorine) in the system apatite-melt. Data include representative images of each experiment, together with a description of run conditions as documented in an accompanying manuscript by Riker et al. (submitted).
 BGS Data Catalogue
BGS Data Catalogue